What are Omega 3s and where are they found?
Omega 3 fatty acids, n-3 Poly-unsaturated fatty acids (n-3 PUFAs), are a type of lipid synthesized by phytoplankton and algae that all marine species accumulate along the trophic chain (figure 2).
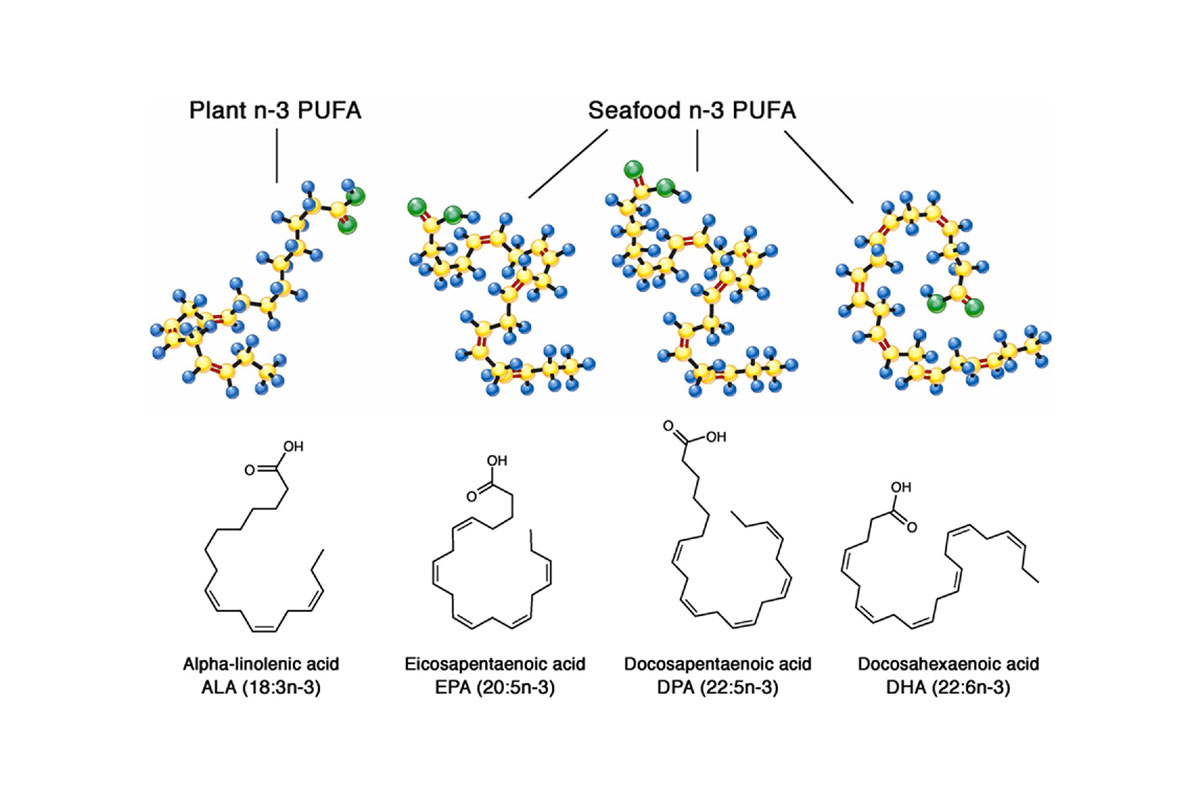
Omega 3 fatty acids are essential fatty acids that our body cannot synthesize and we can only incorporate them into our body through the diet, with the intake of fish, shellfish and algae in the form of Eicosapentaenoic acid and Docosahexaenoic acid (EPA and DHA respectively), as well as some seeds and oils that come from terrestrial vegetables, such as walnuts, flax seeds, rapeseed or soy in the form of Alpha Linoleic acid (ALA).
.jpg)


















