Fish Consumption, Omega 3 and Human Health
Many scientific studies show that Omega 3 fatty acids help reduce inflammatory processes, contribute to skeletal health and play a fundamental role in the development of the structure and function of the brain, as they are key components of brain tissue.
The incorporation of natural Omega 3 fatty acids of marine origin has many benefits against cardiovascular diseases, the leading cause of mortality in the world, in people with coronary diseases. The positive effects observed of a diet with a high intake of Omega 3 in some neurological and psychiatric conditions are being investigated, such as the risk of suffering from Alzheimer's, dementia and cognitive decline, psychotic disorders, depression, schizophrenia, anxiety and other conditions related to social behavior.
The possible beneficial action of Omega 3 in the prevention of other diseases such as cystic fibrosis and hematological diseases is also being studied.
Epidemiological evidence indicates that fish consumption is not associated with an increased risk of cancer of any kind, but high fish consumption could have potential benefits against liver cancer and gastrointestinal cancer, colorectal cancer in particular. However, more studies are needed to determine the possible role of Omega 3 against other types of cancer, such as breast cancer, within the Mediterranean diet.
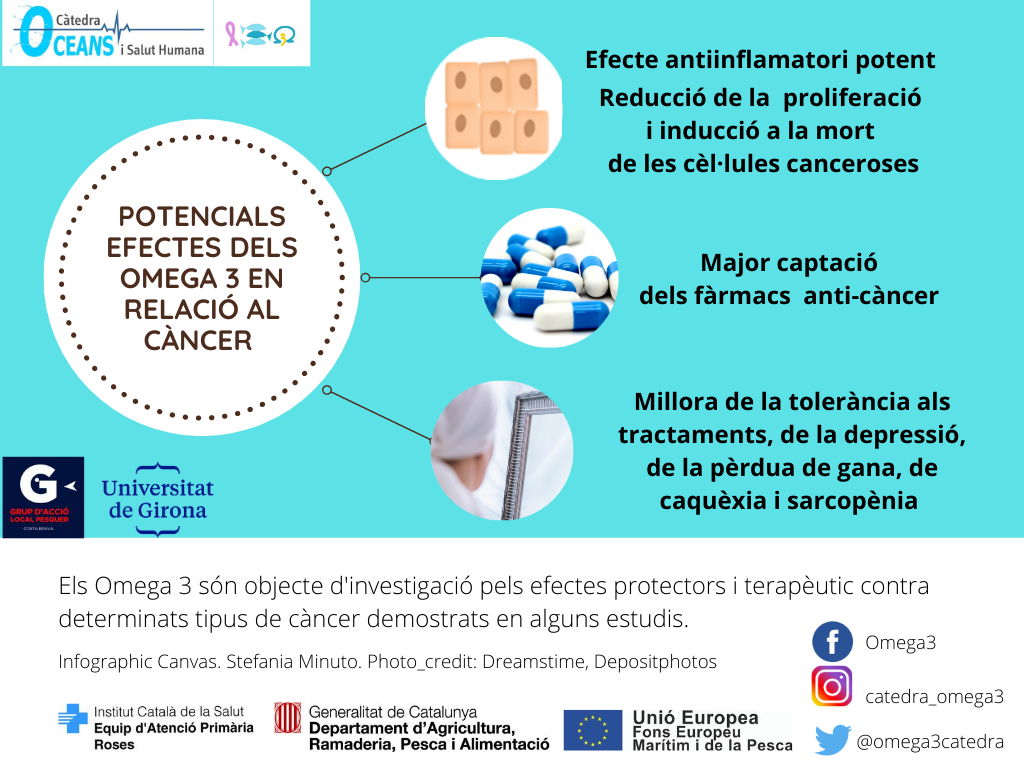
The effect of Omega 3 on certain types of cancer is related to their ability to modulate genes expression involved in cancer pathogenesis and to suppress systemic inflammation. They act specifically in the following ways:
- Powerful anti-inflammatory effect. Potential reduction in the proliferation capacity and induction of cancer cell death.
- They can potentially improve the uptake of the anticancer drugs administered.
- Potential prevention or improvement of problems associated with the disease: improvement in tolerance to treatments, improvement in associated depression, improvement in loss of appetite and the effects of cachexia and sarcopenia associated with cancer.